
Are you planning to travel abroad? Are you looking to buy a new smartphone? One of the biggest shifts in the smartphone industry is the rapid adoption of eSIM technology. As of 2025, more than 60% of smartphones sold worldwide are estimated to support eSIM. In this article, we compare eSIMs and physical SIMs to help you determine which option is best for you. Let’s deep-dive into eSIMs with the experts at ESIMJAPAN.com.
Key difference between eSIM and Physical SIM
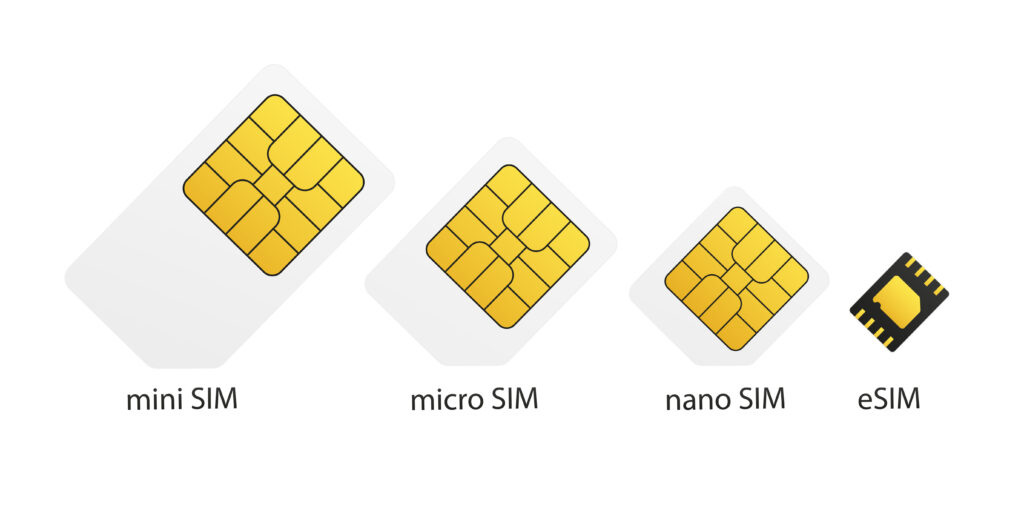
Structural Differences (External Physical card vs Embedded card)
Physical SIM is the small plastic chip we are all familiar with, which you insert directly into your phone’s SIM tray. This card stores two important information: the IMSI (International Mobile Subscriber Identity) and the ICCID (Integrated Circuit Card Identifier).
An eSIM (embedded SIM) is a digital SIM built directly into the smartphone’s internal motherboard. It enables you to store and manage carrier information in software, eliminating the need for a physical card. Standardization efforts were led by the GSMA (Global System for Mobile Communications Association) in 2016, and the technology began to spread widely after Apple introduced the iPhone XS/XR in 2018.
Network Connection Method
Both SIMs connect to the same network carrier, so the network quality and speed are identical. The difference lies in how the mobile service is activated (provisioning process). With a physical SIM, you need to visit a store or receive the SIM by mail and insert it manually. In contrast, eSIM can be activated remotely within minutes by scanning a QR code or using a carrier app. In emergencies, an eSIM can be purchased instantly, while a physical SIM requires waiting for store assistance or delivery.
Convenience of Switching and Transferring
A physical SIM is very easy to move between devices. Simply remove it from the SIM tray and insert it into another phone. This is especially useful if you regularly switch between multiple devices. However, a physical SIM can be easily lost, which may lead to immediate service disruption and the risk of unauthorized access.
Transferring an eSIM, however, is a more complex process. You must undergo a re-provisioning process using a carrier app or customer support. That said, the latest iPhones (iOS 16 and later) and many Android devices now support eSIM Quick Transfer, which significantly simplifies and speeds up this process.
Advantages of eSIM

Instant activation via remote setup
The biggest advantage of eSIM is that it can be activated instantly. By scanning the QR code or entering the provided activation code, you can connect to a network within minutes. When travelling abroad, you can activate a local data plan before boarding the plane, and you’ll be connected as soon as you arrive.
Space-saving improves device design
Without the need for a physical SIM tray, eSIM technology saves valuable internal space within smartphones. Manufacturers can use this extra space to install larger batteries, enhance camera systems, or add additional sensors. For example, the iPhone 17 series features an eSIM-only design that enhances a larger battery capacity.
Easy management of multiple lines
A single device can store over 8 eSIM profiles, with up to 2 active simultaneously (dual eSIM). iPhone 13 and later, as well as the Galaxy 24 series, support Multi eSIM Profile (MEP) functionality, allowing two eSIMs to be used simultaneously without a physical SIM. This makes it convenient to manage both work and personal numbers on one device or to keep your home number while adding a local data plan when traveling.
Enhanced security
eSIMs are embedded within the device, eliminating the risk of physical theft or cloning. Unlike physical SIM cards, which can be removed and inserted into another device, allowing attackers to intercept SMS messages or one-time passwords through SMS swap attacks. On the other hand, eSIM provides strong protection against such threats. Additionally, carriers can manage eSIM settings remotely via OTA (Over-The-Air) updates, enabling quick issue resolutions and further securing the user experience.
Disadvantages of eSIM
Regional and Carrier Restrictions
As of 2025, most major carriers support eSIM, but some regional carriers or MVNOs (Mobile Virtual Network Operators) may not yet offer eSIM services. For instance, eSIM use in mainland China is still limited due to national regulations. Additionally, in some countries, switching eSIMs between carriers can be restricted. For example, some countries require users to delete their existing eSIM before obtaining a new one when changing carriers, thus complicating seamless carrier transactions.
Device compatibility limitation
Not all smartphones support eSIM. Models released before 2018, budget devices, and some mid-range Android phones may lack eSIM capability. In the used phone market and among devices priced under $100, physical SIMs remain the default option, with some devices still being incompatible with eSIM.
Complexity of initial setup
Some users might find the eSIM activation process more complicated than simply inserting a physical SIM card. It may require scanning a QR code, entering the SM-DP+ address (Subscription Manager Data Preparation Address), and configuring the APN (Access Point Name). Additionally, if you lose your device, transferring the eSIM to a new device often requires contacting the carrier’s customer support, making it more time-consuming compared to the straightforward physical removal and reinsertion of a physical SIM.
Advantages of Physical SIM

Universality – Compatible with all devices
The biggest advantage of a physical SIM is its versatility. It has been in use since the 1990s and is compatible with virtually every phone released over the past 20 years. As long as the SIM size (Standard, Micro, Nano) is compatible, it can be used in any device.
Easy mobility between devices
If you regularly switch between devices or need to test multiple gadgets, a physical SIM can simply be removed from the SIM tray and inserted into another device. There is no need for carrier approval or a complicated reactivation process, making physical SIMs very convenient for quick device change.
Ease of Issue Identification
When connectivity issues occur, a physical SIM can be quickly removed and reinserted or tested in a different device. This allows you to rapidly determine whether the problem lies with the SIM or your device.
Disadvantages of Physical SIM
Risk of loss and damage
Physical SIM cards are small, thin plastic chips that can be easily lost or damaged. During replacement, they might be dropped, exposed to water, or have their metal contacts scratched, which can prevent them from working properly
Design constraints
As smartphones become thinner and waterproofing becomes increasingly important, the SIM tray possesses great design limitations. The SIM slot takes up space inside the device and requires additional sealing for water resistance.
Inconvenience of replacement and activation
Changing carriers or obtaining a new number often requires visiting a store or receiving a SIM card by mail. While traveling abroad, you may need to see a local store to purchase a SIM, which can be cumbersome due to language barriers and unfamiliar procedures.
Security Vulnerability
Physical SIM cards are susceptible to SIM swap attacks, where someone physically steals your SIM or tricks a carrier employee into transferring your number to a new SIM. This allows attackers to bypass SMS-based two-factor authentication (2FA), posing significant risks to financial security.
Environmental Impact
Hundreds of millions of plastic SIM cards are produced and discarded each year. When considering packaging and shipping, the environmental burden is substantial. eSIMs help reduce plastic waste and carbon emissions in transportation, making them a more eco-friendly alternative.
Current Status of eSIM-Supported Phones (as of November 2025)
iPhone models eSIM-supported Models

Apple is the manufacturer with the most devices that support eSIM. All iPhones released since the iPhone XR and XS in 2018 support eSIM.
List of eSIM-supported iPhones:
- iPhone Air
- iPhone 17, 17 Pro, 17 Pro Max
- iPhone 16, 16 Plus, 16 Pro, 16 Pro Max
- iPhone 15, 15 Plus, 15 Pro, 15 Pro Max
- iPhone 14, 14 Plus, 14 Pro, 14 Pro Max
- iPhone SE3 (2022)
- iPhone 13, 13 Pro, 13 Pro Max, 13 Mini
- iPhone 12, 12 Pro, 12 Pro Max, 12 Mini
- iPhone 11, 11 Pro, 11 Pro Max
- iPhone SE2 (2020)
- iPhone XR, iPhone XS, XS Max
Recommended iOS version: iOS 13.3 or later
Special features:
- From iPhone 13 onwards: Support dual eSIM functionality (can use two eSIMs simultaneously without a physical SIM)
- From iPhone 14 (US model): eSIM-only design (physical SIM slot completely removed)
- Can store up to 8 eSIM profiles, with up to 2 active at a time.
Important: iPhone 14 and later models sold in the United States are fully eSIM-only with no physical SIM slot. The same models purchased in other countries may still include a physical SIM slot.
Samsung Galaxy eSIM-supported Models

Samsung began releasing models that support eSIMs two years later than Apple, starting in 2020. The global release versions have eSIM support since the Galaxy S20 series.
List of eSIM-supported Galaxy models:
- Galaxy S25 5G, S25 Ultra 5G, S25+ 5G
- Galaxy S24 5G, S24 Ultra 5G, S24+ 5G, S24 FE
- Galaxy S23 5G, S23 Ultra 5G, S23+ 5G
- Galaxy S22 5G, S22 Ultra 5G, S22+ 5G
- Galaxy S21 5G, S21 Ultra 5G, S21+ 5G
- Galaxy S20, S20+, S20 Ultra 5G
- Galaxy Note 20, Note 20 Ultra, Note 20 Ultra 5G
- Galaxy Note 20+, Note 20 FE, Note 20 FE 5G
- Galaxy Fold, Z Fold 2, Z Fold 3, Z Fold 4 5G, Z Fold 5, Z Fold 6, Z Fold 7
- Galaxy Z Flip, Z Flip 3 5G, Z Flip 4 5G, Z Flip 5, Z Flip 6, Z Flip 7
- Galaxy A23 5G, A35 5G, A54 5G, A55 5G
Caution: Some Samsung models sold in the US (e.g., Verizon and AT&T versions) may be carrier-locked but automatically unlock after 60 days.
Special features:
- From the Galaxy S24 series onward: Supports MEP (Multi-SIM Profile), allowing two eSIMs to be active simultaneously.
- eSIM support may vary by carrier for models released in the United States.
Google Pixel eSIM-supported Models

Google is one of the first manufacturers, alongside Apple, to support eSIM. The Pixel 2, released in 2017, was the first smartphone to support eSIM.
List of eSIM-supported Google Pixel models:
- Pixel 9 Pro Fold, 9 Pro XL, 9 Pro, 9
- Pixel 8 Pro, 8a, 8
- Pixel Fold (the first foldable Pixel)
- Pixel 7 Pro, 7a, 7
- Pixel 6 Pro, 6a, 6
- Pixel 5a, 5
- Pixel 4 XL, 4a, 4
- Pixel 3, 3 XL, 3a, 3a XL (limited support)
Exclusion Criteria:
Pixel 3 models manufactured in Australia, Taiwan, and Japan, Pixel 3 models bought from US or Canadian carriers other than Sprint and Google Fi, and Pixel 3a models bought in Southeast Asia and with Verizon service do not support eSIM functions.
Note: Pixel devices purchased from Verizon are carrier-locked for 60 days after purchase, after which they unlock automatically
Other manufacturers
Motorola eSIM-supported Models:
- Moto G, G85, G55, G54, G53 5G, G35
- Moto G Power
- Moto G Stylus 5G
- Edge 50 Fusion, 50 Pro, 50 Neo, 50 Ultra
- Edge 40 Pro, 40 Neo
- Edge+
- Razr 40 Ultra
- Razr 2024
- Razr+ 2024
- Razr 2022
- Razr 2019
- Razr 5G
- Razr 50
- ThinkPhone 25
Note: Motorola products purchased from mainland China, Hong Kong, and Macao do not support eSIM.
Xiaomi eSIM-supported Models:
- Xiaomi 15
- Xiaomi 14, 14 Pro, 14T, 14T Pro
- Xiaomi 13, 13 Lite, 13 Pro, 13T, 13T Pro
- Xiaomi 12T Pro
- Redmi Note 14 Pro, 14 Pro+
- Redmi Note 13 Pro, 13 Pro +
- Redmi Note 11 Pro 5G
OnePlus eSIM-supported Models:
- OnePlus 13
- OnePlus 12
- OnePlus 11
Note: OnePlus products purchased from mainland China, Hong Kong, and Macao do not support eSIM.
eSIM vs Physical SIM: Which one should you choose?
When to choose eSIM
Highly Recommended For:
- Frequent international travelers: data plans can be activated even before arriving at the destination.
- Need for work and personal numbers separately: you can manage on a single device via dual eSIM.
- Latest version smartphone users: iPhone 13 and later, and Galaxy S24 and later.
2025 Trends
- Over 60% of smartphones sold worldwide are compatible with eSIM.
- iPhone 14 and later models sold in the United States are eSIM-only.
- More than 2 billion eSIM-supported devices are expected to be released by 2025.
- Physical SIM cards are expected to be phased out within the next five years.
Tips for User
- Use a secure, strong internet connection while at home or in your home country to pre-activate your eSIM. This will ensure you have a seamless network experience as soon as you arrive at your destination.
- Before installation, ensure that you turn off VPNs and proxy connections.
- Check device compatibility before purchasing an eSIM. For detailed information on device compatibility, visit our website.
When to choose physical eSIM
Recommended For:
- Users of devices released before 2018.
- Those who frequently switch between multiple devices and need an easy transfer.
- Users of mid-range smartphones, especially those priced under $100, generally do not support eSIM.
- Residents in regions where carriers do not support eSIM.
- Individuals who prefer simple methods and are not comfortable with technology.
Hybrid Approach (recommended)
The best choice:
- Primary line (home number): Use either a Physical SIM or an eSIM, depending on your carrier
- Secondary line (for travel or work): Utilize eSIM
This approach allows you to enjoy the benefits of both technologies. Maintain stability with your primary line while flexibly adding or removing eSIMs for travel or special purposes.
Conclusion: The Future of SIM Technology—Embracing eSIM
In the evolving landscape of mobile technology, both eSIM and physical SIM cards offer unique benefits and challenges. As technological advancements accelerate and countries like the USA fully adopt eSIM, alongside the rise of IoT devices fundamentally built on eSIM technology, the widespread adoption of eSIM is rapidly approaching. This transformative technology promises to be seamlessly integrated into many aspects of our daily lives soon.
For travelers, especially those heading to destinations like Japan, exploring ESIMJAPAN.com‘s diverse data pricing plans is highly recommended. With high-speed data options and unlimited plans covering more than 200 countries, including Japan, eSIM ensures instant connectivity without the hassle of swapping physical cards.




Leave a Reply